Environmental Report 2011
Measures against Climate Change
The fight against climate change is a crucial global issue that requires the further involvement of each and every person and organization. The JAE Group is working to address climate change through the teaching of environmental awareness, production-related measures, and measures at plant facilities, and it has set definite objectives and targets for its environmental activities. The Group's FY 2010 activities are characterized by its teaching of and activities for energy-saving awareness among its employees via the establishment of its Ten-Point Plan for Saving Energy.Status of Response to Common Target of Electrical/Electronics Industries
Total CO2 emissions from the domestic JAE Group in FY 2010 were 30,668 tons, a 6.5% increase over the previous fiscal year.This increase in emissions was due to increased production resulting from an improving economy when compared to FY 2009.
The JAE Group is involved in a variety of measures to meet the electrical/electronics industry's common target under the voluntary action plan advocated by the Japan Business Federation, i.e., a 35% reduction from FY 1990 in the average emissions per unit of real sales by 2010. Its efforts have resulted in a 39% reduction.
CO2 emissions due to energy use per unit of real sales
Change in domestic JAE Group average emissions per unit of real sales
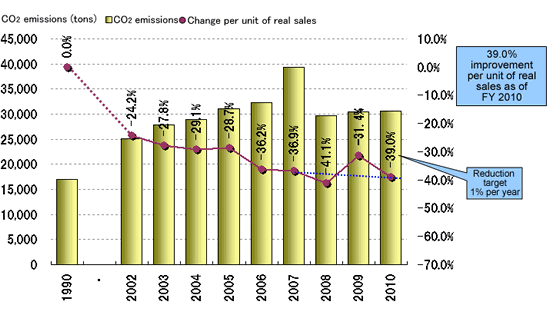
*Average CO2 emissions per unit of real sales = CO2 emissions divided by real sales.
Real sales is an indicator adjusted for the steep drop in prices in the electrical/electronics industry, and is obtained by dividing sales by the Bank of Japan's domestic corporate goods price index (in the field of electrical equipment).
Real sales = sales divided by the domestic corporate goods price index (electrical equipment)
*The equivalency factor for CO2 emissions due to energy use is the value published by the Federation of Electric Power Companies. In FY 2010, the FY 2009 result (0.351tons-CO2/MWh) is being used.
Status of Response to Tokyo Cap-and-Trade Program
The Tokyo Cap-and-Trade Program for greenhouse gas emissions at large plants located in Tokyo kicked off on April 1, 2010.The program targets plants in Tokyo that have a large amount of CO2 emissions (about 1,400 plants). The Akishima Plant was designated as a special climate change countermeasure plant under the program, and it is obligated to cut emissions by an average of 6% during the first phase from FY 2010 to FY 2014, with average CO2 emissions from FY 2005 to FY 2007 (approximately 10,389 tons) set as the baseline.
In the first phase, JAE expects to be able to achieve it reduction obligations through its own efforts, which include a five-year production plan and plan for addressing climate change. FY 2010 emissions were reduced some 15% from the standard emission value, enabling a reduction beyond the initial plan.
Grassroots Campaign for Saving Energy
The JAE Group has long been involved in energy-saving activities as part of its environmental management activities, but demands for saving energy are becoming even more strident worldwide. Under such circumstances, the Group has started a grassroots campaign, believing that every person associated with JAE must make a steady effort, including at home, to save energy.An outline of the main activities deployed thus far as part of this grassroots effort is provided below.
●Formulation of Ten-Point Plan for Saving Energy
The Ten-Point Plan for Saving Energy was formulated as a basic action plan for implementing energy-saving activities. It is intended to broadly deploy energy-saving activities. Energy-saving activities, not only at the company, but also at home, are expanding the energy-saving effect and raising individual awareness. The Ten-Point Plan for Saving Energy also includes energy-saving measures to be carried out at home. An energy-saving effect table was also released to employees in order to make it easier for them to get an actual sense of the effects per energy-saving measure.

●e-learning targeting all employees
Education on saving energy was carried out for all employees of the JAE Group in order to widely deploy energy-saving activities at the individual level. This education was implemented with the same content and at the same time period for employees at all companies and all sales sites. The educational content included in the Ten-Point Plan for Saving Energy as well as energy saving measures that can be applied at home. Since an extremely large number of employees had to be educated, e-learning by PC was utilized. Courses were given in February 2011 and not a single employee was left out. The company was able to achieve the objective of the grass-roots movement of widely deploying energy-saving activities at the individual level.

●Implementation of measures based on Ten-Point Plan for Saving Energy
To implement thorough energy savings, an in-depth review of energy-saving measures was carried out across the entire company based on energy-saving activities so far, and the energy-saving measures that were deemed feasible were implemented. Examples of those that were implemented at production facilities are given here.
- Review lighting in all workplaces (turn lights off until the necessary level of lighting is achieved)
- Thoroughly control temperature in all workplaces (Cool Biz during the summer)
- Review cafeteria lighting (turn lights off until the necessary level of lighting is achieved)
- Review elevator use (take some elevators out of service)
- Turn off toilet warming (water temperature and toilet seat)

●Confirmation of implementation status of measures
Periodic energy-saving patrols are being conducted by taking a photometer and thermometer (and in production departments, an air leakage detector) into each department to ensure thorough implementation of measures, and further energy-saving proposals are being made to departments that require them.
Other Main Energy-Saving Measures in FY 2010
Examples of product-related energy-saving measures
- Saving energy by increasing the production efficiency of pressing and plating processes (JAE)
- Saving energy by improving the aging process (JAE)
- Saving energy by improving air leak (JAE)
- Saving energy by stopping clean room ventilation at night and on days off (JAE)
- Saving energy by increasing use of efficient vacuum pump equipment (HAE, YAE)
Continuing from last year, the amount of electric power used is being cut by increasing the number of units in operation and their operating time for equipment that was modified from factory air to vacuum pumps.

Energy savings at plant facilities
- Further removal of fluorescent lamps (all sites)
- Renovation of lighting facilities (JAE)
Converted 350 fluorescent lighting fixtures from copper/iron ballasts to inverter ballasts, and a further 280 from FLR40W2 lamps to energy-saving 40W1 lamps. - Review of uninterruptible power supplies (UPS) (JAE)
Halted operation of aging centralized CVCF UPS systems, and reviewed the entire UPS system, installing UPS units only in server rooms where they are essential.
