Environmental Report 2012
Zero Emissions
The JAE Group makes effective use of resources by reducing general waste by consuming less paper, while promoting recycling and sale of valuable resources through the exhaustive sorting of waste, such as scrap plastic and metal.Zero Emissions Activities
After launching its zero emissions efforts in FY 2000, JAE achieved a recycling rate of 99% in FY 2004, and kept it at the 99% level thereafter.Thanks to the JAE Group�s efforts to promote the sale of plastic and metal waste, the sales rate of all valuable resources has exceeded 60% since FY 2006. In addition to reducing costs for waste treatment, the sale of valuable waste contributes to resource saving and the reduction of CO2 over the life cycle of products. The Group aims to achieve even higher rates of sales.Note: The JAE Group defines zero emissions as achieving a recycling rate of 99% or higher for waste defined by local ordinances, excluding waste that is disposed of by incineration and simple landfills.
Change in Waste Treatment
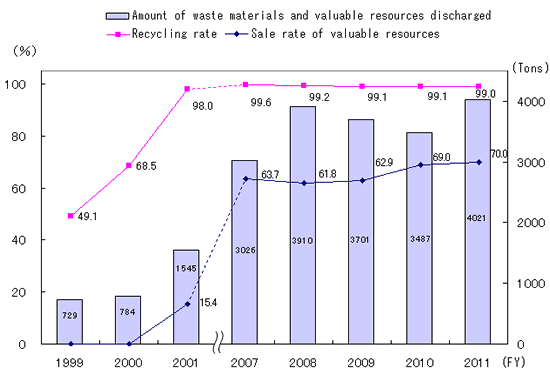
(Note: Valuable resources are not included in the FY 1999 and 2000 figures.)
Efforts for Proper Disposal of Waste Materials
The JAE Group is implementing proper disposal of waste materials in accordance with Japan's Waste Disposal Law. The Group conducts compliance studies on subcontractors that handle all types of industrial waste, general waste, and valuable resources at the time of contract signing and periodically thereafter by periodically checking their licenses and performing on-site inspections.

Main Activities in FY 2011
- Promoting the recovery of valuable waste plastics (JAE, HAE, YAE)
The JAE Group is striving to improve the sales rate of waste plastics by thoroughly sorting them during recovery promoting reuse within the company, liaising with recycling firms, and other measures. - Recovery of Ni from plating sludge (HAE)
In FY 2011, the company began recovering Ni from plating sludge, contributing to cost reduction through the double effect of reducing waste processing expenses and sale of the resource. - Reduction of glass sludge (JAE)
Improving the efficiency of the glass manufacturing process and fully drying waste products contribute both to reducing the amount of glass sludge and reducing the amount of glass raw material. - Recycling cleaning fluids (YAE)
To promote the recycling of cleaning fluids, the company completely separated the recovery of waste oil and waste fluids and redefined them as saleable substances, rather than waste, reducing waste to zero. - Reducing waste by lowering process defects (HAE, YAE, SAE)
The company is cutting waste by reducing the rate of defects, setting targets for the process defect rate and so on. In FY 2011, the defect rate was reduced in line with the target by improving quality and workability through measures such as upgrading tools and procedures, reinforcing component target value management, and enhancing the skills of workers. This resulted in commensurate waste reductions.The company will continue its efforts toward eradicating defects and promoting manufacturing that is environmentally friendly.