Environmental Report 2017
Chemical Substance Management
Improving chemical substance management
In consideration of workers’ safety and health, and looking to lower environmental impact, we are making efforts to improve the management of chemical substances. Here, we introduce initiatives undertaken by the JAE Group in Japan, and individual case studies about sites around the country.across the JAE Group in Japan
◆GHS(*use the cursor to view definition) symbol education
To prevent disasters, secure safety, preserve the environment, and provide information to users, JAE conducted e-learning concerning GHS symbols for operators and managers of chemical substances. This education was provided to 151 people at the JAE,HAE,YAE,FAE,SAE sites in fiscal 2016. Since starting in fiscal 2014, we have educated a total of 1,836 people. JAE continuously strives to provide information on dangerously toxic substances.

JAE Site
◆substances
First, here is an explanation of chemical substance registration.
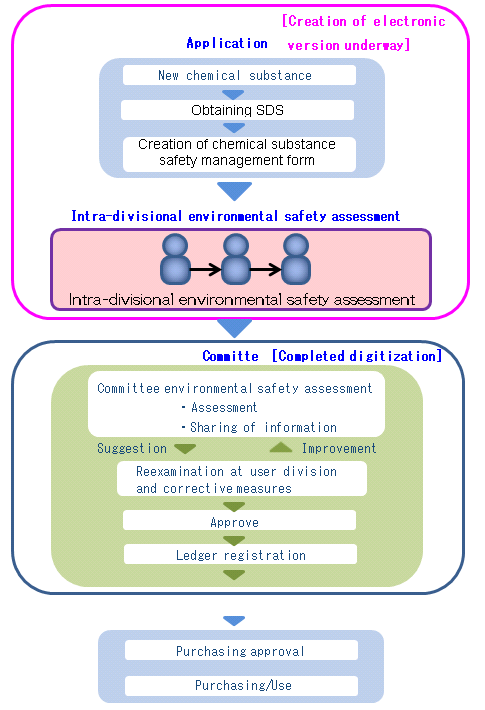
The introduction of a new chemical substance or piece of equipment, construction work, disposal of waste, or unscheduled operations thought to present safety problems or another issue, require an environmental safety assessment under JAE's in-house pre-assessment system, as shown in the flowchart below. With regard to the use of chemical substances, a chemical substance safety management form is prepared, and assessment is made, with the entry of requisite information on items including transport, storage, handling, and disposal of chemical substances.
Given this, chemical substances can only be purchased if they pass this assessment.
■Pre-assessment flowchart for new chemical substances following the environmental safety assessment
The environmental safety assessment at JAE sites, comprising internal division assessments and committee assessments, has since 2012 seen an electronic version of the committee assessment for increased efficiency. With the aim of creating greater efficiency, sharing information among auditors, and improving the level of knowledge, we are integrating internal audits with committee audits and are working to create a totally electronic version of environmental safety assessments in fiscal 2017.
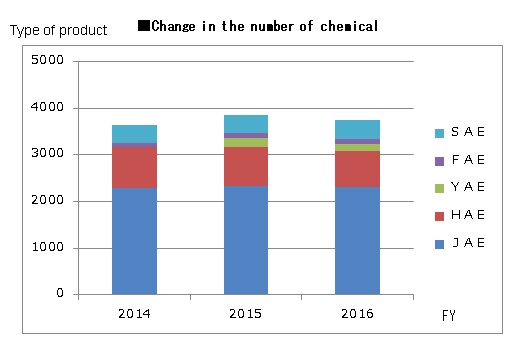
Monitoring registration of chemical substance product types
Change in the number of chemical substance product types at five sites in Japan is as visualized in the below graph. The reason that the JAE site has more chemical substances than other sites is because it is not only involved in production, but is also a development plant and uses chemical substances for testing. YAE has begun to aggregate data from 2015.The JAE Group continues to work hard to cut types of unnecessary chemical substances and to reduce the volume of chemical substances, as shown below.
Reduction of Chemical Substances
As in the previous fiscal year, in fiscal 2016 each production site selected specific chemicals and worked to reduce the amount used in order to reduce its environmental impact. The main points of the activities for reducing the use of chemicals in fiscal 2016 are shown below, and these reduction efforts will continue in the coming years.
Note that the letters in parentheses, such as JAE, HAE, YAE, FAE and SAE, are abbreviations denoting sites that carried out these activities.
| JAE: |
|
| HAE: |
|
| YAE: |
|
| SAE: |
|
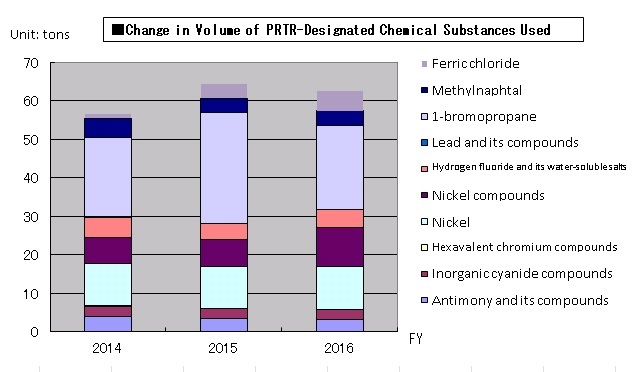
PRTR Data
The graph below shows the change in the amount of chemicals subject to the PRTR(*use the cursor to view definition) that was used by five sites in Japan.Fiscal 2016 saw an increase in ferric chloride used in nickel compounds associated with plating and liquid waste treatment, which was due to increased production volumes. The decrease in 1-bromopropane contained in cleaning agents was due to lower production of target items and upgrading cleaning agents. There was also a reduction in the volume of methylnaphtalen, a component of heavy oil used in boilers, owing to removal of boilers and switching to air-cooled heat pumps, which cut crude oil. The JAE Group’s efforts to identify trends with regard to the handling of PRTR volumes are ongoing.
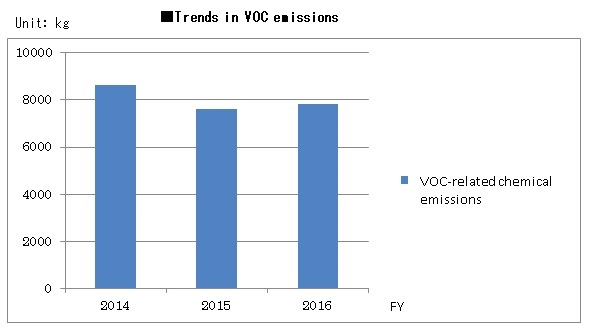
VOC Information
The JAE Group has been reducing VOC-related chemical emissions each year, primarily of alcohol and other cleaning fluids. We are striving to reduce VOC (*use the cursor to view definition) emissions by improving the airtightness of containers and promoting the use of non-VOC cleaning fluids, but emissions increased due to higher production in fiscal 2016. The total volume of chemical emissions of VOCs and related substances for five combined sites in Japan is shown in the below graph. We will continue to monitor as we strive to reduce chemical emissions into the environment.