Environmental Report 2016
Reducing Usage of Materials
Reducing Usage of Materials
In an effort to use materials more efficiently, measures that reduce the amount (percentage) that becomes waste after being introduced into the manufacturing stage are being promoted. An introduction to efforts at each site to use the main materials more effectively is provided below.●Efforts at JAE site
In order to reduce the volume of gold used in gold plating, JAE is making ongoing efforts to implement efficient improvements in such areas as the management of proper metal plating fields. In addition, to reduce the volume of materials used in machine processing, JAE is moving forward on purchasing in accordance with proper dimensions.
●Efforts at HAE site
HAE is focusing on reduction of the amount of materials used by reducing the width of metal materials used in presses and pin protection materials. The reduction of molding materials is being achieved by reducing unnecessary spoolers/runners (*use cursor to view definitions) that are discharged when extracting molded products; improving the number gates(*use cursor to view definitions), mold shape, and positioning when designing molds; and switching from cold runners to hot runners. This reduces the amount of molding material used, while using recycled materials reduces the amount of newly purchased material inputs.
●Efforts at YAE site
Measures are underway for reducing the amount of materials used and waste generated by downsizing molds and revising the width of metal materials used in presses. In addition, reusing molding material leads to reduce input materials and making spoolers/runners more compact cuts down on the volume of materials used, which in turn results in significant CO2 reductions.
●Efforts at FAE site
Efforts to improve the reuse rate for copper alloy electrode material used in the manufacturing process for metal parts (discharge machining) are contributing to a reduction in the quantity of material used and the metal waste generated.
●Efforts at SAE site
The SAE site continues to focus on self-production of machined parts and reducing cutting processes. These efforts contribute to reduced metal waste, as well as lower CO2 emissions during material production.
Conservation of Water Resources
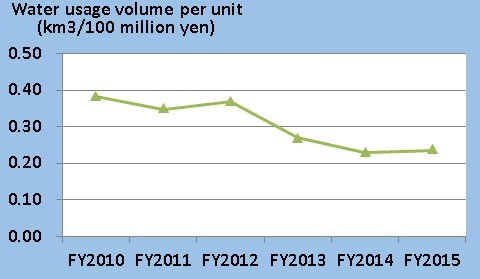
Japan may appear to be a country with abundant water resources, but it is actually said to be the world's largest importer of virtual water (*use the cursor to view definition). Around the world, we see explosive population growth as well as drought and other abnormal weather conditions that result in many people being unable to obtain one-tenth of the daily water that a person requires.This section introduces a number of the activities of the JAE Group, both in and outside of Japan, designed to reduce the volume of water resources used, as well as other efforts, including forest preservation and river and shoreline cleanup activities.
- Water saving in production: recycling water in the connector product plating line and on/off controls for water usage on each cleaning line. Also limiting users in processes where large volumes of water are required for cleaning, and specialized faucets that are opened with keys.
- Water saving in lifestyle: adjusting water volume used in air conditioning cooling towers, recycling wastewater, using rainwater for toilets, using cooling tower drain water for toilets, changing from buried pipes that supply water for living to above-ground piping for the early detection of leaks and repair, and raising awareness of an important resource.
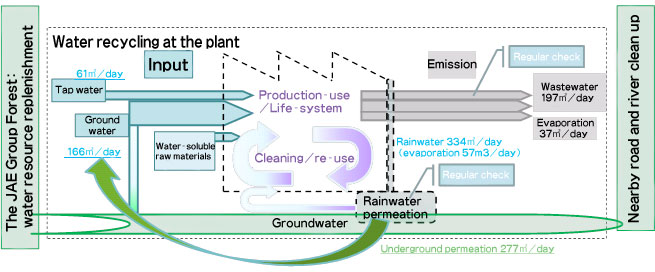
Visualization of water resource balance
For measures that will further conserve water and to assess water-related risk, we confirmed the water resource balance of the JAE site (Akishima Plant), which seeks to obtain 70% of the water it uses from groundwater (see diagram).
Upon considering the correlation of trends and production volumes in each fiscal year, and measures to conserve water, and other factors, we have gained an understanding of a number of data points for analysis. However, through the rainwater storage and permeation tank,*1 we were also able to confirm that it would be possible to replenish more groundwater than is actually used.
*1: In the vicinity of the Akishima Plant, heavy rains cause the streets to flood, affecting the people of the local community. For that reason, 15 years ago we installed a rainwater storage and permeation tank underneath the employee parking lot, which solved the flooding problem.