Environmental Report 2012
Reducing Environmental Risks
Prevention of Soil and Groundwater Pollution
The discovery of soil and groundwater contaminated with hazardous substances is on the rise in Japan due to the redevelopment of former plant sites and voluntary surveys. Since countermeasures after contamination has already occurred take a vast amount of time and money, this is gaining recognition every year as a massive social problem, and related laws and regulations are being put in place.Amid these developments, Japan's Water Quality Pollution Control Act was amended in 1989 and 1996 in an effort to strengthen measures against groundwater pollution, and in 2002, the Soil Contamination Countermeasures Act was issued. Then, in June 2011, the Water Quality Pollution Control Act was amended, strengthening regulations for preventing contamination of ground water. The requirements of businesses that handle harmful substances and facilities that cause contamination are becoming more stringent every year.
The JAE Group has been preventing contamination by such means as double-walling underground storage facilities and pipes, but in FY 2010, it went even further by launching efforts to assess the risks of leaks and seepage into the soil at facilities that handle hazardous substances and those that handle fuel oil. The company has worked to prevent contamination from FY 2011 with a focus on responding to the amended Water Quality Pollution Control Act.
* To learn more about what the JAE Group is doing, refer to "Special Feature: Responses to the Amended Water Quality Pollution Control Act."
Chemical Substance Management
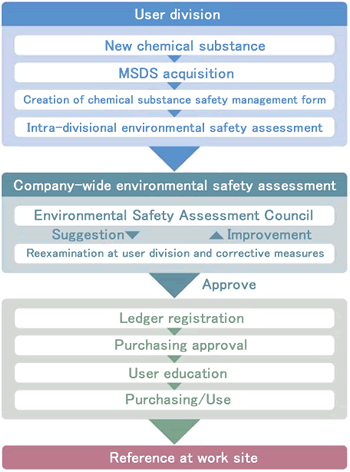
The introduction of a new chemical substance or piece of equipment, construction work, increased waste volume, and other changes require an environmental safety assessment under JAE's in-house pre-assessment system. For chemical substances, it has prepared an ad hoc chemical substance safety management form for the entry of requisite information on items including transport, storage, handling, and disposal. New chemical substances in particular can only be purchased if they pass this assessment. The pre-assessment flow for new chemical substances is shown below.The following table presents data for the chemical substances registered as of FY 2011. Many chemicals are inspected and registered for R&D and improving processes. Last year the number of registrations increased, but the company will also actively implement cuts in chemicals that are no longer needed.
■JAE Akishima Plant
| 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number registered | 2,249 | 2,183 | 2,218 |
| Discontinued | 52 | 172 | 67 |
| New | 84 | 107 | 102 |
| Number of distinct chemical substances registered | 1,753 | 1,782 | 1,801 |
■Pre-assessment flowchart for new chemical substances
The registration of chemicals is managed in a chemicals database. From FY 2011, JAE (Akishima) has computerized the chemical component data in the MSDS, and the system went into operation in May 2012.
This has simplified searching for chemical components that are subject to amended regulations, and chemicals will be managed with this system henceforward.
Reduction of Chemical Substances
As in the previous fiscal year, in FY 2011 each production site selected specific chemicals and worked to reduce the amount used in order to reduce its environmental impact. The main points of the activities for reducing the use of chemicals in FY 2011 were as follows.- Reduction of the metal used for deposition in gold plating (JAE)
- Reduction of the amount of cleaning fluid used by improving the washing method (JAE, YAE)
- Reduction of atmospheric VOC emissions by improving the seal of the container, using a better washing method, and reducing the amount of new purchases (JAE, YAE)
- Reduction of the amount of chemicals used by introducing new facilities and lowering the amount of new purchases (HAE, YAE)
- Reduction of carbon dioxide gas use by introducing new facilities (SAE)
PRTR Data
Japan's revised PRTR Law was promulgated in 2008. This changed the kinds of chemical substances that are targeted by the law, and starting on April 1, 2010, the JAE Group began identifying the newly targeted substances it was using. The amount of methylnaphthalene contained in bunker A (fuel oil) used in boilers and n-Propyl bromide contained in cleaning fluid for metal parts exceeded one ton in 2011 again, which meant they were subject to PRTR reporting. Reports were filed by electronic and other means.The following table shows the change in substances subject to reporting and the amount of such substances used that were subject to RoHS directives. These figures are the combined value of five domestic manufacturing companies, and the ★ marks correspond to the number of production sites that were subject to PRTR reporting. Antimony and its compounds were used in the material for forming connectors (antimony trioxide) due to their fire resistance, but starting in FY 2009, the JAE Group began reducing antimony and its compounds by switching to other materials. The Group had also been reducing hexavalent chromium and lead, which are substances subject to RoHS directives, for several years.Reductions have leveled out over the past several years, but this is due to the Group's response to the demands of customers for uses that are not subject to RoHS. Since reducing waste is also crucial in dealing with PRTR-targeted chemical substances, the Group is promoting recycling and working to identify trends.
■Change in Volume of PRTR-Designated Chemical Substances Used Unit: tons
| Fiscal | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Antimony and its compounds | ★★19.9 | ★★4.9 | ★2.4 | ★2.2 |
| Inorganic cyanide compounds | ★2.1 | ★1.8 | ★2.8 | ★2.1 |
| Hexavalent chromium compounds | 0.14 | 0.15 | 0.18 | 0.12 |
| Nickel | ★5.8 | ★6.0 | ★6.4 | ★8.0 |
| Nickel compounds | ★1.9 | ★2.5 | ★2.9 | ★4.0 |
| Hydrogen fluoride and its water-soluble salts | ★★4.6 | ★3.4 | ★★4.5 | ★★4.4 |
| Lead and its compounds | 0.30 | 0.10 | 0.16 | 0.10 |
| n-Propyl bromide | - | - | ★★★8.9 | ★★★8.4 |
| Methylnaphthalene | - | - | ★★★★8.6 | ★★★★9.0 |